Map Of North China Plain
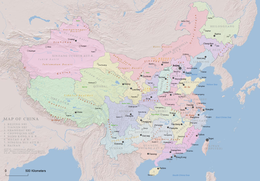 | |
| Continent | Asia |
|---|---|
| Region | East/Southeast Asia |
| Coordinates | 35°0′N 105°0′E / 35.000°Northward 105.000°E / 35.000; 105.000 [one] |
| Area | Ranked 3 |
| • Full | 9,596,960[1] kmtwo (iii,705,410 sq mi) |
| • Land | 97.2[1]% |
| • Water | two.eight[1]% |
| Coastline | 14,500[1] km (nine,000 mi) |
| Borders | Afghanistan, Bhutan, Burma, Bharat, N Korea, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Laos, Mongolia, Nepal, Islamic republic of pakistan, Russia, Tajikistan, Vietnam |
| Highest point | Mount Everest, 8,848 m (29,029 ft)[2] |
| Everyman point | Turpan Pendi, −154 1000 (−505 ft)[1] |
| Longest river | Yangtze River[3] |
| Largest lake | Qinghai Lake[ citation needed ] |
| Climate | various; ranges from tropical in south to subarctic in north[i] |
| Terrain | generally mountains, high plateaus, deserts in west and plains, deltas and hills in e[1] |
| Natural resources | coal, fe ore, petroleum, natural gas, mercury, tin, tungsten, antimony, manganese, molybdenum, vanadium, magnetite, aluminum, lead, zinc, rare earth elements, uranium, hydropower potential, arable land[1] |
| Natural hazards | typhoons; damaging floods; tsunamis; earthquakes; droughts; land subsidence[i] |
| Ecology problems | air pollution; water shortages; water pollution; deforestation; soil erosion; desertification; trade in endangered species[1] |

Satellite imagery of Red china




Communist china has keen physical diversity. The eastern plains and southern coasts of the country consist of fertile lowlands and foothills. They are the location of most of Red china's agricultural output and human population. The southern areas of the country (South of the Yangtze River) consist of hilly and mountainous terrain. The w and north of the country are dominated past sunken basins (such equally the Gobi and the Taklamakan), rolling plateaus, and towering massifs. It contains part of the highest tableland on earth, the Tibetan Plateau, and has much lower agronomical potential and population.
Traditionally, the Chinese population centered on the Chinese fundamental plain and oriented itself toward its own enormous inland market, developing equally an purple power whose center lay in the middle and lower reaches of the Xanthous River on the northern plains.[ commendation needed ] More recently, the 18,000 km (11,000 mi) coastline has been used extensively for export-oriented merchandise, causing the coastal provinces to go the leading economical heart.
The People's Republic of China has an area of virtually 9,600,000 km2 (three,700,000 sq mi). The exact country area is sometimes challenged by border disputes, most notably about Taiwan, Aksai Chin, the Trans-Karakoram Tract, and Southward Tibet. The area of the People'southward Republic of People's republic of china is 9,596,960 km2 (3,705,410 sq mi) according to the CIA's The World Factbook.[1] The People'south Democracy of China is either the third or fourth largest country in the world, beingness either slightly larger or slightly smaller than the United States depending on how the area of the United States is measured. Both countries are smaller than Russia and Canada and larger than Brazil.
Physical Geography [edit]
Generalities [edit]

Traditional physical and cultural divisions of China

The topography of China has been divided by the Chinese government into five homogeneous physical macro-regions, namely Eastern Prc (subdivided into the northeast plain, north plain, and southern hills), Xinjiang-Mongolia, and the Tibetan highlands.[4] It is various with snow-capped mountains, deep river valleys, broad basins, high plateaus, rolling plains, terraced hills, sandy dunes with many other geographic features and other landforms present in myriad variations. In general, the land is high in the westward and descends to the east declension. Mountains (33 percent), plateaus (26 percent) and hills (10 pct) account for nearly 70 per centum of the country's land surface. Most of the country's arable land and population are based in lowland plains (12 per centum) and basins (19 percentage), though some of the greatest basins are filled with deserts. The country's rugged terrain presents bug for the structure of overland transportation infrastructure and requires all-encompassing terracing to sustain agriculture, just is conducive to the evolution of forestry, mineral and hydropower resources, and tourism.
Eastern Mainland china [edit]
- Northeast Plain
Northeast of Shanhaiguan a narrow sliver of flat littoral land opens up into the vast Northeast Red china Manifestly. The plains extend north to the crown of the "Chinese rooster," near where the Greater and Lesser Hinggan ranges converge. The Changbai Mountains to the east divide Red china from the Korean peninsula. Compared with the rest of the area of Mainland china, here live the most Chinese people due to its adequate climate and topography.
- Northward evidently
The Taihang Mountains form the western side of the triangular North Prc Apparently. The other two sides are the Pacific coast to the east and the Yangtze River to the southwest. The vertices of this triangle are Beijing to the north, Shanghai to the southeast, and Yichang to the southwest. This alluvial plain, fed by the Yellowish and Yangtze Rivers, is one of the most heavily populated regions of Cathay. The only mountains in the plain are the Taishan in Shandong and Dabie Mountains of Anhui.
Beijing, at the north tip of the North China Plain, is shielded by the intersection of the Taihang and Yan Mountains. Further north are the drier grasslands of the Inner Mongolian Plateau, traditionally home to pastoralists. To the s are agricultural regions, traditionally dwelling house to sedentary populations. The Groovy Wall of China was congenital in the mountains across the mountains that mark the southern edge of the Inner Mongolian Plateau. The Ming-era walls run over 2,000 km (1,200 mi) e to west from Shanhaiguan on the Bohai coast to the Hexi Corridor in Gansu.
- Due south (hills)
E of the Tibetan Plateau, deeply folded mountains fan out toward the Sichuan Basin, which is ringed by mountains with ane,000–3,000 m height. The floor of the basin has an average elevation of 500 m and is dwelling to one of the most densely farmed and populated regions of China. The Sichuan Basin is capped in the north past the eastward continuation of the Kunlun range, the Qinling, and the Dabashan. The Qinling and Dabashan ranges form a major north-south divide across Communist china Proper, the traditional core surface area of China. Southeast of the Tibetan Plateau and south of the Sichuan Basin is the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, which occupies much of southwest China. This plateau, with an average elevation of 2,000 m, is known for its limestone karst landscape.
South of the Yangtze, the landscape is more rugged. Like Shanxi Province to the n, Hunan and Jiangxi each accept a provincial core in a river bowl that is surrounded by mountains. The Wuling range separates Guizhou from Hunan. The Luoxiao and Jinggang dissever Hunan from Jiangxi, which is separated from Fujian by the Wuyi Mountains. The southeast littoral provinces, Zhejiang, Fujian and Guangdong, have rugged coasts, with pockets of lowland and mountainous interior. The Nanling, an east-due west mountain range across northern Guangdong, seals off Hunan and Jiangxi from Guangdong.
Xinjiang-Mongolia [edit]
Northwest of the Tibetan Plateau, between the northern slope of Kunlun and southern slope of Tian Shan, is the vast Tarim Bowl of Xinjiang, which contains the Taklamakan Desert. The Tarim Basin, the largest in China, measures 1,500 km (930 mi) from east to west and 600 km (370 mi) from north to due south at its widest parts. Average elevation in the basin is 1,000 1000. To the east, the basin descends into the Hami-Turpan Depression of eastern Xinjiang, where the dried lake bed of Lake Ayding, at −154m beneath sea level, is the lowest surface point in China and the third-everyman in the world. With temperatures that have reached 49.half-dozen C., the lake bed ranks every bit ane of the hottest places in China. North of Tian Shan is Xinjiang's second great basin, the Junggar, which contains the Gurbantünggüt Desert. The Junggar Basin is enclosed to the north past the Altay Mountains, which separate Xinjiang from Russia and Mongolia.
Northeast of the Tibetan Plateau, the Altun Shan-Qilian Mountains range branches off the Kunlun and creates a parallel mountain range running east-west. In between in northern Qinghai is the Qaidam Basin, with elevations of 2,600–3,000 m and numerous brackish and table salt lakes. North of the Qilian is Hexi Corridor of Gansu, a natural passage between Xinjiang and China Proper that was role of the ancient Silk Road and traversed by modern highway and runway lines to Xinjiang. Farther north, the Inner Mongolian Plateau, between 900–1,500 m in peak, arcs north up the spine of China and becomes the Greater Hinggan Range of Northeast China.
Between the Qinling and the Inner Mongolian Plateau is Loess Plateau, the largest of its kind in the world, covering 650,000 km2 (250,000 sq mi) in Shaanxi, parts of Gansu and Shanxi provinces, and some of Ningxia-Hui Autonomous Region. The plateau is 1,000–ane,500m in summit and is filled with loess, a yellow, loose soil that travels hands in the wind. Eroded loess silt gives the Yellow River its colour and name. The Loess Plateau is jump to the east by the Luliang Mount of Shanxi, which has a narrow basin running n to south along the Fen River. Further east are the Taihang Mountains of Hebei, the dominant topographical feature of North China.

.


- Highlands
The world'southward tallest mountains, the Karakorum, Pamirs and Tian Shan divide China from Southward and Cardinal Asia. 11 of the seventeen tallest mountain peaks on Earth are located on China'southward western borders. They include the globe'southward tallest peak Mt. Everest (8848 yard) in the Himalayas on the border with Nepal and the globe'south 2d tallest height, K2 (8611 thou) on the border with Pakistan. From these towering heights in the w, the country descends in steps similar a terrace.
North of the Himalayas and eastward of the Karakorum/Pamirs is the vast Tibetan Plateau, the largest and highest plateau in the globe, as well known every bit the "Roof of the World." The plateau has an average height of 4,000 meters higher up ocean level and covers an area of 2.5 million square kilometers, or about one-5th of People's republic of china's land mass. In the north, the plateau is hemmed in by the Kunlun Mountains, which extends eastward from the intersection of the Pamirs, Karakorum and Tian Shan.
- Tallest mountain peaks
Also Mt. Everest and K2, the other nine of the world's 17 tallest peaks on China'due south western borders are: Lhotse (8516 m, quaternary highest), Makalu (8485 m, fifth), Cho Oyu (8188 yard, 6th), Gyachung Kang (7952 thousand, 15th) of the Himalayas on the border with Nepal and Gasherbrum I (8080 m, 11th), Wide Peak (8051 m, 12th), Gasherbrum Ii (8035 m, 13th), Gasherbrum Iii (7946 m, 16th) and Gasherbrum IV (7932 m, 17th) of the Karakorum on the border with Pakistan. The tallest peak entirely within China is Shishapangma (8013 one thousand, 14th) of the Tibetan Himalayas in Nyalam Canton of Tibet Autonomous Region. In all, ix of the xiv mountain peaks in the globe over viii,000 1000 are in or on the edge of Red china. Another notable Himalayan peak in China is Namchabarwa (7782 m, 28th), virtually the great bend of the Yarlungtsanpo (upper Brahmaputra) River in eastern Tibet, and considered to be the eastern anchor of the Himalayas.
Outside the Himalayas and Karakorum, China's tallest peaks are Kongur Tagh (7649 chiliad, 37th) and Muztagh Ata (7546 1000, 43rd) in the Pamirs of western Xinjiang, Gongga Shan (7556 m, 41st) in the Great Snowy Mountains of western Sichuan; and Tömür Shan (7439 m, 60th), the highest pinnacle of Tian Shan, on the edge with Kyrgyzstan.
Rivers [edit]

Prc originally had an estimated number of fifty,000 rivers. Nevertheless, due to statistical discrepancies, water and soil loss, and climate change, there are currently but an estimated 22,000 rivers remaining.[five] The rivers in Mainland china accept a total length of 420,000 kilometers. 1,500 have a catchment surface area exceeding 1,000 square kilometers. The majority of rivers flow west to east into the Pacific Ocean. The Yangtze (Chang Jiang) rises in Tibet, flows through Central China and enters the E Prc Sea nearly Shanghai. The Yangtze is 6,300 kilometers long and has a catchment area of ane.8 million square kilometers. It is the third longest river in the world, subsequently the Amazon and the Nile. The 2d longest river in Mainland china is the Huang He (Yellow River). It rises in Tibet and travels circuitously for 5,464 kilometers through North China, information technology empties into the Bo Hai Gulf on the north coast of the Shandong Province. It has a catchment area of 752,000 foursquare kilometers. The Heilongjiang (Heilong or Black Dragon River) flows for 3,101 kilometers in Northeast China and an additional 1,249 kilometers in Russia, where it is known every bit the Amur. The longest river in South China is the Zhujiang (Pearl River), which is 2,214 kilometers long. Along with its three tributaries, the Xi (Westward), Dong (East), and Bei (North) rivers, it forms the Pearl River Delta nearly Guangzhou, Zhuhai, Macau, and Hong Kong. Other major rivers are the Liaohe in the northeast, Haihe in the due north, Qiantang in the eastward, and Lancang in the southwest.

Inland drainage involving upland basins in the due north and northeast accounts for forty percentage of the country'southward total drainage expanse. Many rivers and streams flow into lakes or diminish in the desert. Some are used for irrigation.
Mainland china'south territorial waters are principally marginal seas of the western Pacific Sea. These waters prevarication on the indented coastline of the mainland and approximately 5,000 islands. The Yellow Body of water, Eastward China Sea, and S Mainland china Sea are marginal seas of the Pacific Ocean. More than half the coastline, predominantly in the south, is rocky; most of the remainder is sandy. The Bay of Hangzhou roughly divides the two kinds of shoreline.
- Northern plain
In that location is a steep driblet in the river level in the North Mainland china Plain, where the river continues across the delta, information technology transports a heavy load of sand and mud which is deposited on the flat plain. The flow is aided by manmade embankments. As a result, the river flows on a raised ridge l meters to a higher place the plain. Waterlogging, floods, and grade changes have recurred over the centuries. Traditionally, rulers were judged by their business for or indifference to preservation of the embankments.[ citation needed ] In the modernistic era, China has undertaken all-encompassing flood control and conservation measures.
Flowing from its source in the Qingzang highlands, the Yellow River courses toward the body of water through the North China Plain, the celebrated center of Chinese expansion and influence. Han Chinese people have farmed the rich alluvial soils since ancient times, constructing the K Canal for northward-south transport during the Majestic Era. The apparently is a continuation of the Dongbei (Manchurian) Obviously to the northeast but is separated from it by the Bohai Gulf, an extension of the Xanthous Sea.
Like other densely populated areas of China, the plain is bailiwick to floods and earthquakes. The mining and industrial center of Tangshan, 165 km (103 mi) eastward of Beijing, was leveled by an earthquake in July 1976, information technology was believed to be the largest earthquake of the 20th century by death toll.
The Hai River, similar the Pearl River, flows from west to eastward. Its upper course consists of five rivers that converge near Tianjin, and so flow seventy kilometers earlier elimination into the Bohai Gulf. The Huai River, rises in Henan Province and flows through several lakes before joining the Pearl River near Yangzhou.
- E and Yangtze
The Qin Mountains, a continuation of the Kunlun Mountains, divides the North China Patently from the Yangtze River Delta and is the major physiographic boundary between the ii great parts of Cathay Proper. It is a cultural boundary as it influences the distribution of customs and linguistic communication. South of the Qinling mountain range split are the densely populated and highly developed areas of the lower and centre plains of the Yangtze River and, on its upper reaches, the Sichuan Basin, an area encircled by a loftier bulwark of mountain ranges.
The country's longest and most important waterway, the Yangtze River, is navigable for the majority of its length and has a vast hydroelectric potential. Rising on the Qingzang Plateau, the Yangtze River traverses 6,300 km (3,900 mi) through the eye of the country, draining an area of 1,800,000 kmtwo (690,000 sq mi) before elimination into the East China Body of water. Roughly 300 million people live forth its middle and lower reaches. The area is a large producer of rice and wheat. The Sichuan Bowl, due to its mild, humid climate and long growing season, produces a variety of crops. It is a leading silk-producing area and an of import industrial region with substantial mineral resources.
The Nanling Mountains, the southernmost of the east-west mountain ranges, overlook areas in China with a tropical climate. The climate allows two crops of rice to be grown per year. Southeast of the mountains lies a littoral, hilly region of small deltas and narrow valley plains. The drainage expanse of the Pearl River and its associated network of rivers occupies much of the region to the s. West of the Nanling, the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau rises in two steps, averaging i,200 and 1,800 m in elevation, respectively, toward the abrupt mountain regions of the eastern Qingzang Plateau.
Geology and natural resource [edit]
China has substantial mineral reserves and is the globe'south largest producer of antimony, natural graphite, tungsten, and zinc. Other major minerals are aluminum, bauxite, coal, rough petroleum, diamonds, golden, atomic number 26 ore, atomic number 82, magnetite, manganese, mercury, molybdenum, natural gas, phosphate stone, tin, uranium, and vanadium. China's hydropower potential is the largest in the world.
Land use [edit]
Based on 2005 estimates, 14.86% (about 1,400,000 km2 (540,000 sq mi)) of Communist china's total land expanse is arable. About 1.3% (some 116,580 km²) is planted to permanent crops and the rest planted to temporary crops. With comparatively little country planted to permanent crops, intensive agricultural techniques are used to reap harvests that are sufficient to feed the earth's largest population and still take surplus for export. An estimated 544,784 km² of land were irrigated in 2004. 42.9% of total land area was used as pasture, and 17.5% was forest.
Wild fauna [edit]
Cathay lies in two of the world's major ecozones, the Palearctic and the Indomalaya. In the Palearctic zone mammals such as the horse, camel, and jerboa are found. Amid the species constitute in the Indomalaya region are the leopard cat, bamboo rat, treeshrew, and diverse other species of monkeys and apes. Some overlap exists betwixt the two regions considering of natural dispersal and migration, and deer or antelope, bears, wolves, pigs, and rodents are found in all of the diverse climatic and geological environments. The famous behemothic panda is institute merely in a limited area along the Yangtze. In that location is a standing trouble with merchandise in endangered species, although at that place are at present laws to prohibit such activities.
Human geography [edit]
History [edit]

The Primal patently, visible in dark orangish
Chinese history is often explained in terms of several strategic areas, defined by particular topographic limits. Starting from the Chinese central plain, the quondam eye of the Han populations, the Han people expanded militarily so demographically toward the Loess Plateau, the Sichuan Bowl, and the Southern Hills (as defined by the map on the left), not without resistance from local populations. Pushed by its comparatively higher demographic growth, the Han continued their expansion by armed services and demographic waves. The far-southward of present-day China, the northern parts of today'south Vietnam, and the Tarim Bowl were first reached and durably subdued by the Han dynasty's armies. The Northern steppes were e'er the source of invasions into People's republic of china, which culminated in the 13th century by Mongolian conquest of the whole China and creation of Mongolian Yuan dynasty. Manchuria, much of today's Northeast China, and Korean Peninsula were normally not under Chinese control, with the exception of some limited periods of occupation. Manchuria became strongly integrated into the Chinese empire during the belatedly Qing dynasty, while the w side of the Changbai Mountains, formerly the home of Korean tribes, thus also entered Cathay.
Demographic geography [edit]

A population density map of the territories governed past the China and the ROC. The eastern, littoral provinces are much more densely populated than the western interior considering of the historical access to h2o.
The demographic occupation follows the topography and availability of former abundant lands. The Heihe–Tengchong Line, running from Heihe, Heilongjiang to Tengchong County, Yunnan divides Communist china into two roughly equal sections–in terms of geographic area, with areas west of the line existence sparsely settled and areas east densely populated, in full general. Today there are 5 major religions that accept been recognized past the country; Buddhism, Taoism, Protestantism, Catholicism, and Islam. Buddhism and folk religions account for roughly 21% of the population while protestants make up v% and Islam ane.6% of the population.[6] A substantial number of Buddhists live in the southwestern Tibetan region of the country which borders Nepal, Bangladesh, and Bhutan and near notably India, the birthplace of Buddhism. The Islamic population, consisting mostly of Hui and Uighur Muslims, is full-bodied in the northwestern Xinjiang region of the country which shares borders with Mongolia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, Islamic republic of pakistan, Republic of india, and Russian federation.[seven]
Administrative geography [edit]
Chinese administrative geography was drawn mainly during the 1949 and 1954 administrative reorganizations. These reorganizations have been the source of much contend within China. In addition, a bundle of land was ceded from Guangdong to Guangxi to grant the latter immediate access to the Gulf of Tonkin, while Hainan was split from Guangdong in 1988 and Chongqing from Sichuan in 1997.
Agriculture [edit]
As the state continues to industrialize, the share of agriculture equally a role of Prc's GDP has lowered to 11% in contempo years. Of the enormous labor force in China, 27.7% work in agronomics.[eight] China's master agronomical import is wheat from Argentine republic, Commonwealth of australia, Canada, and France. They import about four to v million metric tons of wheat per year and they are able to buy the wheat for about $70 per ton, making wheat China's about of import agricultural import. On the other hand, Cathay's most important agricultural export is rice. China exports about 750,000 metric tons of rice per year for nearly $120 per ton.[9] Other significant agricultural exports from China are potatoes, corn, tobacco, peanuts, tea, apples, cotton wool, pork, mutton, eggs, fish, and shrimp.[8]
According to the World Bank, as of 2015, People's republic of china'southward full abundant land was estimated at 119,000,000 hectares.[10] Since 2005, arable country in Communist china has been on the pass up and the total abundant land per citizen has reached .two acres.[11] As a percentage, agricultural land makes up about 54.7% of country. The climate of the state is hard to draw because it varies then much depending on the region of Communist china. The southernmost parts of the country are almost tropical, while the northernmost part is subarctic.[12]
Click any region for more info. For a larger version of this map, meet here.


Boundary disputes [edit]
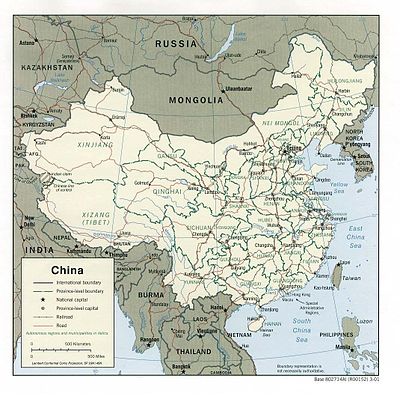
Map of the People's Commonwealth of China (click to enlarge), source: CIA
Territory [edit]
The territory of China has been divers every bit a homeland for many different indigenous and racial groups in the country. However, the style that the territory has been divers varies between ethnic groups. In relation to the Han Chinese, the homeland has been defined by national borders which are more or less accepted internationally. This is because the Han Chinese are the largest population and have about influence politically than any other ethnic population in Mainland china. To the Han Chinese population, the territory of the country is divers by the regions of Tibet, inner Mongolia, Manchuria, and the Xinjiang Province which is the nearly western land of China. The Chinese territory is the 2nd largest in state area and also has the longest combined land edge in the world. However, there are many other ethnic groups in China that have their ain definitions of what concerns the territory of China.
One group of people in Cathay are the Tibetans. Tibetans and the country of Tibet are considered by the Han Chinese government to be part of Mainland china and that the territory of Tibet is also function of the land. However, many Tibetans disagree and are protesting as well as rallying for freedom in present day. To this indigenous population, the territory of Tibet is not considered part of Mainland china and and so is not divers as a Chinese territory. However, the Chinese government still consider Tibet as a territory of Communist china which reflects the dispute in definition of Chinese territory between two ethnic groups.
Another group of people which take a dispute in definition of territory are the Taiwanese. The Taiwanese people inhabit the island of Taiwan and are markedly politically dissimilar as the people of Taiwan take a free market place capitalist based economy while the mainland Chinese government use a communistic land run economy. At that place are disputes in the definition of territory betwixt Taiwan and Communist china every bit the Chinese government claims buying over Taiwan while some Taiwanese people maintain that they are a sovereign state completely independent from the mainland Chinese government. These disputes have led to international controversy as many countries such as the United States of America accept non officially recognized the sovereignty of Taiwan.[13]
Central Asia [edit]
China's borders take more than 20,000 km (12,000 mi) of land frontier shared with nearly all the nations of mainland East Asia, and have been disputed at a number of points. In the western sector, China claimed portions of the 41,000 km2 (16,000 sq mi) Pamir Mountains area, a region of soaring mount peaks and glacier-filled valleys where the borders of Afghanistan, Pakistan, the old Soviet Spousal relationship, and China come across in Cardinal Asia. North and east of this region, some sections of the border remained undemarcated in 1987. The 6,542 kilometres (4,065 mi) frontier with the Soviet Marriage has been a source of continual friction. In 1954 China published maps showing substantial portions of Soviet Siberian territory equally its own. In the northeast, edge friction with the Soviet Matrimony produced a tense situation in remote regions of Inner Mongolia and Heilongjiang along segments of the Argun River, Amur River, and Ussuri River. Each side had massed troops and had exchanged charges of edge provocation in this area. In a September 1986 oral communication in Vladivostok, the Soviet leader Mikhail Due south. Gorbachev offered the Chinese a more conciliatory position on Sino-Soviet border bug. In 1987 the ii sides resumed edge talks that had been cleaved off after the 1979 Soviet invasion of Transitional islamic state of afghanistan (see Sino-Soviet relations). Although the border outcome remained unresolved as of late 1987, Cathay and the Soviet Matrimony agreed to consider the northeastern sector commencement. In Oct 2004, China signed an agreement with Russia on the delimitation of their unabridged 4,300 km (2,700 mi)-long border, which had long been in dispute.
Southern border [edit]
Eastward from Bhutan and northward of the Brahmaputra River (Yarlung Zangbo Jiang) lies a large expanse controlled and administered by Republic of india simply claimed past the Chinese. The area was demarcated by the British McMahon Line, fatigued forth the Himalayas in 1914 every bit the Sino-Indian border; India accepts and China rejects this purlieus. In June 1980 China made its first movement in twenty years to settle the border disputes with India, proposing that Republic of india cede the Aksai Chin area in Jammu and Kashmir to Prc in return for China'south recognition of the McMahon Line; Republic of india did not accept the offer, withal, preferring a sector-by-sector approach to the problem. In July 1986 Prc and India held their seventh circular of border talks, just they made piffling headway toward resolving the dispute. Each side, but primarily India, continued to make allegations of incursions into its territory by the other. Near of the mountainous and militarized boundary with Bharat is still in dispute, simply Beijing and New Delhi accept committed to brainstorm resolution with discussions on the least disputed middle sector. India does non recognize Pakistan'south ceding lands to Cathay in a 1964 boundary agreement.
The China-Burma edge issue was settled 1 Oct 1960, by the signing of the Sino-Burmese Boundary Treaty. The first joint inspection of the border was completed successfully in June 1986.
India: On xv May 2015, Mr. Li from China and Mr. Modi from India held talks at the Bully Hall of the people during Modi's Cathay tour. The 2 leaders held talks on border disputes that began in 1914 when the British withal controlled Republic of india and signed an agreement with Tibet to make the McMahon line the de-facto boundary betwixt Republic of india and China, fifty-fifty though China had rejected this agreement. Both countries had various claims to disputed territories such as the S Tibetan region of Zangnan which is considered to be part of the Arunachal Pradesh land in India. So far there have been only talks and no solutions and tensions continue to rise as each country continues to increment regional influences.[14]
Seas [edit]
China is involved in a complex dispute with Malaysia, Philippines, Vietnam, and mayhap Brunei over the Spratly (Nansha) Islands in the S China Ocean. The 2002 "Announcement on the Conduct of Parties in the Due south China Sea" eased tensions but fell brusk of a legally binding code of comport desired by several of the disputants. China also controls the Paracel (Xisha) Islands, which are also claimed by Vietnam, and asserts a claim to the Japanese-administered Senkaku (Diaoyu) Islands in the East Cathay Body of water.
South Cathay Bounding main: On 16 June 2011, the Chinese government sent out one of its largest patrol ships known as the Haixun-31 which the Chinese government depict every bit routine. The ship will pass the Paracel and Spratly Islands and make its way upwardly from the Malaysian to Filipino declension. Vietnam, Cathay, the Philippines, Taiwan, Brunei and Malaysia all accept competing claims to the Spratlys Islands while Beijing and Hanoi are in dispute over the Paracel islands. Hanoi has proposed a multilateral solution between the Asian countries but China says that it prefers to negotiate with private states separately.[15]
Border security [edit]
The security and forcefulness of the Chinese borders vary depending on the location of the section of the border in question. This is due to the nature of the borders as well as the physical geography of the country. China has a large territory, about the aforementioned size every bit the United States, but the bodily distribution of population is highly disproportionate. 60 percent of the population live on the east coast of China which is just 22 percent of its territory while the other 78 percent lying inland is sparsely populated with indigenous minorities such as Tibetans, Kazakhs, Uighurs, and other Chinese Muslim groups. Many of these groups have piffling to no loyalty to the central regime of Communist china further adding to the strained security of Mainland china'due south borders. The regions of Xinjiang and Tibet in particular harbor strong separatist movements[xiii]
Tibet: Many Tibetans protest and actively support the Dalai Lama who lives in exile in what he calls "democratic Tibet". The Chinese regime charge him of promoting Tibetan independence and will not allow him to come dorsum into the country or he volition face up abort. In May 2018, a Tibetan activist known as Tashi Wangchuk was sentenced to prison for five years equally he voiced his concerns over that Tibetan culture was being destroyed by the Chinese regime. Immunity International denounced this sentencing to be "beyond absurd" only his release is still dated to be in 2021.[sixteen]
Xinjiang: In the region of Xinjiang, Uighur separatists have engaged in acts of violence to promote independence. These Chinese Muslims have garnered support from neighboring areas in central Asia and Turkey both politically and economically. Withal, many of these efforts have been close down past Chinese officials. The Xinjiang region is facing large scale immigration of Han Chinese people simply the Uighurs yet make upwardly 8 out of the 19 1000000 inhabitants. In August 2018, a UN human being rights panel cited "creditable reports" that more than i 1000000 people in the region were beingness held in counter extremism centers in Xinjiang but Chinese officials claimed that only "religious extremist" Uighurs were undergoing re-education and resettlement.[17]
People's republic of china-Russia Relations: China and the Soviet Union signed an brotherhood in 1950 building on their communist relations that dated back to the 1920'southward. In the wake of the 1960'southward Sino-Soviet split, and for 25 years after the split, the border betwixt Communist china and Russia was i of the virtually unfriendly borders in the world. At one point over "1 and a half million troops armed with nuclear weapons" were installed forth the two sides of the border. Relations improved in the mid 1980's but this is due to Russia's decrease in ability and threat to the Chinese government.[thirteen]
Due to Red china's ancient history and cardinal location in the geography of Asia, it is surrounded past potential enemies and many complicated rivalries. The government plays the fine line between domination and cooperation in social club to preserve their national identity and borders. However, due to the nature of their political geography, the borders are very much volatile and disputes continue to exist in different areas of the border.
Tajikistan: On 13 January 2011, the land of Tajikistan agrees to sacrifice land to the Chinese government. The Tajik parliament voted to ratify a 1999 deal to cede 1000 foursquare kilometers of land in the remote Pamir Mountain range which the Chinese merits thoroughly resolved the century long border dispute. China is the largest investor in the Tajik economy especially in the energy and infrastructure sectors.[eighteen]
Authorities Construction [edit]
The structure of government in Red china is in the framework of a socialist republic which is run past a single party: the Communist Party of Prc. The political party wishes to control and manage the ideology of their subjects to maintain their political dominance in China. For example, Document Number Nine, or the Communiqué on the Current State of the Ideological Sphere, was a document circulated in Communist china in 2013 to warn the citizens of China against some western values such as media freedom. General Secretary of the Communist Party of People's republic of china is leader of the Chinese Communist Party. Currently Xi Jinping is the Party general secretary, making him the Paramount leader of China.[xix] The National People's Congress is the national legislature and the highest organ of state power. [20]
The government is divided into three primary groups of state power: the National People's Congress (NPC), the President, and the State Council. Members of the State Quango include the Premier, four vice premiers, five state councilors and 29 heads of State Quango commissions. Under the Chinese constitution, the National Peoples congress holds the near power and meets annually for 2 weeks to discuss and review legislative policies.[21]
As Red china has only one ascendant party, the spatial patterns of voting and ballot results are favoring the ascendant communist party. Even so, the state still has some other variables and variations in the divisions of administration. Local government is divided into four levels of hierarchy. Local government includes township, county, prefecture or municipality, and the province every bit the scope of government increases. Mainland china also has a system of autonomous regions intended to requite more than command to ethnic minorities who preside in those regions. In practice still, the power still remains with the party secretary while the local chairman is the nominal caput.[22]
Imperialism [edit]
Nippon [edit]
Historically there have been instances of imperialism in China. Nippon had invaded and conquered much of Manchuria and Coastal cities in Cathay in the Sino-Japanese war. Cities such as Nanjing and Hong Kong were devastated by Japanese forces with actions such as massacre and rape of civilians was rampant. This imperialism and invasion of Japanese forces nevertheless leads to tensions in modern day. For case in Apr 2005, a Japanese junior high textbook minimized the atrocities of Nanjing stating that the massacre was an "incident". The textbooks transgression sent thousands of Chinese citizens out to protest and 3 weeks of state sanctioned protestation led to rise tensions between Nihon and China.[23]
Hong Kong and United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland [edit]
Due to the opium wars between the British from 1839 to 1842, the British were able to make demands to the Chinese government before removing blockades and stopping bombardment on cardinal ports. The Chinese agreed to cede the island of Hong Kong which in the command of the British, witnessed phenomenal growth. The population grew from ane,500 to 19,000 by 1844. In 1860 in the wake of the 2d Opium state of war, the Peking convention was signed which ceded to Britain the Kowloon peninsula (up to Boundary Street) and Ngon Sun Chau, which was a function of mainland China. With the end of World War 2 however, the British lost control of the colonies and in 1997, the colony of Hong Kong was returned to the control of communist mainland China.[24]
Trade Agreements [edit]
China has bilateral investment agreements with 100+ countries and economies. China'due south bilateral investment agreements encompass expropriation, arbitration, and other investment related issues. These bilateral agreements are generally much weaker than investment treaties that the Usa would want to negotiate. People's republic of china also maintains fourteen free trade agreements(FTA's) and is currently implementing an additional 8 FTA's. Communist china'southward FTA partners are ASEAN, Singapore, Pakistan, New Zealand, Republic of chile, Republic of peru, Costa rica, Iceland, Switzerland, Hong Kong, Macao, Taiwan, Australia, and Korea. These trade agreements be to maintain and organize business and trade with various countries in order to improve and expand the economy of China.[25]
Population [edit]
China in 2017, was reported to have a population of i,379,302,711.[26] In October 2015, Prc changed the long standing 1979 police force that immune each couple to accept "i kid". So that there would exist enough youth to support the old, the regime began to allow couples to have 2 children. With this rule, the birth rate increased to 12.3 births/1,000 population,[26] and the death rate is reported to be vii.8 deaths/ 1,000 population.[26] Established in 2017, the current population growth is at a .41%.[26]
The current babe bloodshed total rate is 11.8 deaths/1,000 live births.[26] For females the rate is 11.4 deaths/i,000 live births,[26] and the males stand at 12.ii deaths/ 1,000 live births.[26] In 2015 it was established that the maternal mortality rate is 27 deaths/ 100,000 alive births.[26] For both infant and maternal mortality rates, Communist china stands at 118 in comparison to the world.[26]
The people of Prc are starting time to move from the rural farming areas to the business concern centered cities. The charge per unit of urbanization from 2015 to 2018 is at a 2.42% annual rate of change.[26] China currently has an urban population of 59.3%.[26] The almost populated urban areas are: Shanghai 25.582 million,[26] Tianjin 13.215 1000000,[26] Guangdong 12.683 million,[26] xix.618 meg Beijing (upper-case letter),[26] eleven.908 million Shenzhen,[26] xiv.838 1000000 Chongqing.[26]
The life expectancy at nascency for the full population stands at 75.7 years.[26] While men are averaged out at 73.6 years,[26] the woman of China are reported to accept the life expectancy of 78 years.[26]
Historic period Structure [edit]

Shows the historic period structure of Red china
Below a 2016 population pyramid illustrates the population age construction throughout Communist china. It tin exist observed that the youth of China is significantly lower than the working course. However, in that location is enough people in the working form to support the elders at the time. This can help evidence physically the reasoning and push to alter the "one child" 1979 law, to two.
Atmosphere and pollution [edit]
Climate [edit]

Owing to tremendous differences in breadth, longitude, and distance, the climate of Red china is extremely diverse, ranging from tropical in the far south to subarctic in the far north and alpine in the higher elevations of the Tibetan Plateau. Monsoon winds, caused by differences in the heat-absorbing capacity of the continent and the ocean, dominate the climate. During the summer, the E Asian Monsoon carries warm and moist air from the south and delivers the vast majority of the almanac precipitation in much of the country. Conversely, the Siberian anticyclone dominates during winter, bringing common cold and comparatively dry out conditions. The advance and retreat of the monsoons account in large degree for the timing of the rainy flavor throughout the land. Although nigh of the country lies in the temperate belt, its climatic patterns are complex.
The northern extremities of both Heilongjiang and Inner Mongolia take a subarctic climate; in dissimilarity, most of Hainan Isle and parts of the extreme southern fringes of Yunnan accept a tropical climate. Temperature differences in wintertime are considerable, simply in summertime the variance is considerably less. For example, Mohe County, Heilongjiang has a 24-hour average temperature in January approaching −xxx °C (−22 °F), while the corresponding figure in July exceeds 18 °C (64 °F). Past contrast, nearly of Hainan has a January mean in backlog of 17 °C (63 °F), while the July mean there is more often than not to a higher place 28 °C (82 °F).
Precipitation is almost invariably concentrated in the warmer months, though annual totals range from less than twenty millimetres (0.8 in) in northwestern Qinghai and the Turpan Low of Xinjiang to hands exceeding 2,000 millimetres (79 in) in Guangdong, Guangxi, and Hainan. Only in some pockets of the Dzungaria region of Xinjiang is the conspicuous seasonal variation in precipitation that defines Chinese (and, to a large extent, East Asian) climate absent.
Annual sunshine duration ranges from less than i,100 hours in parts of Sichuan and Chongqing to over iii,400 hours in northwestern Qinghai. Seasonal patterns in sunshine vary considerably past region, but overall, the north and the Tibetan Plateau are sunnier than the south of the country.
-

Snow encircling the expanse around the Bo Hai
-

The first 24-hour interval of spring 2010 brought a massive sandstorm blowing from Inner Mongolia
-

On November 11, 2010, a wall of sand blew across northern China, roofing much of the North People's republic of china Plainly and Shandong Peninsula.
-

Smog from Eastern Red china spread over neighboring areas in February 2004.
-

-

Natural color satellite image of a smog event in the heart of northern China
-

Dumbo smog settled over the Due north Prc Plain on February twenty, 2011.
Surround [edit]
Air pollution (sulfur dioxide particulates) from reliance on coal is a major event, along with water pollution from untreated wastes and use of debated standards of pollutant concentration rather than Full Maximum Daily Load. There are water shortages, particularly in the north. The eastern part of China often experiences smoke and dumbo fog in the atmosphere as a upshot of industrial pollution. Heavy deforestation with an estimated loss of one-fifth of agronomical land since 1949 to soil erosion and economic development is occurring with resulting desertification. China is a party to the Antarctic-Ecology Protocol, the Antarctic Treaty, the Convention on Biological Diverseness, the Climatic change treaty, the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification, the Endangered Species treaty, the Chancy Wastes treaty, the Constabulary of the Sea, the International Tropical Timber Agreements of 1983 and 1994, the International Convention for the Regulation of Whaling, and agreements on Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, and Wetlands protection. Cathay has signed, but not ratified, the Kyoto Protocol (only is not yet required to reduce its carbon emission under the agreement, as is Bharat) and the Nuclear Test Ban treaty.
Run into also [edit]
- Chinese geography
- History of human geography in China
- Environment of China
- List of islands of China
- List of rivers in Communist china
- Listing of mountains in China
- Lakes in China
- North Red china Manifestly
- Geography of Hong Kong
- Geography of Macau
- Geographic information systems in China
- Zomia (geography)
Notes and references [edit]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "Cathay". The World Factbook. CIA. Retrieved 31 December 2015.
- ^ Based on the 1999 and 2005 surveys of elevation of snow cap, not rock head. For more than details, see Surveys.
- ^ "Yangtze River". University of Washington. Retrieved 31 December 2015.
- ^ CIA (October 1967), Communist Red china Map Folio, U.S. Central Intelligence Agency
- ^ Miao, Angel Hsu, William (29 April 2013). "28,000 Rivers Disappeared in Communist china: What Happened?". The Atlantic . Retrieved 14 September 2018.
- ^ "The State of Religion in People's republic of china". Quango on Foreign Relations . Retrieved 13 October 2018.
- ^ "This fascinating map shows the new religious breakup in China". Concern Insider . Retrieved 13 Oct 2018.
- ^ a b "Due east Asia/Southeast Asia :: China — The World Factbook - Central Intelligence Agency". www.cia.gov . Retrieved 21 November 2018.
- ^ Mah, Feng-Hwa (1971). "Why China Imports Wheat". The Mainland china Quarterly (45): 116–128. JSTOR 651886.
- ^ "Arable land (hectares) | Data". data.worldbank.org . Retrieved 2 November 2018.
- ^ "Farming the World: China'south Epic Race to Avoid a Food Crisis". Bloomberg. 22 May 2017. Retrieved 29 September 2022.
- ^ "Due east Asia/Southeast Asia :: Prc — The World Factbook - Key Intelligence Agency". www.cia.gov . Retrieved 17 Nov 2018.
- ^ a b c Chung, Jae Ho (21 September 2017). "China Goes Local (Again)". Columbia Academy Press. one. doi:x.7312/columbia/9780231176200.003.0002.
- ^ "India and Red china 'to resolve dispute'". BBC News. 15 May 2015. Retrieved 26 Nov 2018.
- ^ "China sends transport to disputed sea". BBC News. 16 June 2011. Retrieved 26 Nov 2018.
- ^ "Tibet activist jailed after NYT video". BBC News. 22 May 2018. Retrieved 26 November 2018.
- ^ "Xinjiang profile". BBC News. 12 Oct 2018. Retrieved 26 Nov 2018.
- ^ "Tajikistan cedes land to People's republic of china". BBC News. 2011. Retrieved 26 Nov 2018.
- ^ "Cathay'southward 'Chairman of Everything': Behind Xi Jinping's Many Titles". The New York Times. 15 Oct 2017.
Mr. Xi'southward almost of import championship is general secretary, the most powerful position in the Communist Party. In China'southward one-party system, this ranking gives him virtually unchecked authority over the government.
- ^ "Implementation Regulations of the People'southward Republic of China Drug Management Constabulary". Chinese Law & Government. 45 (2): 30–49. March 2012. doi:10.2753/clg0009-4609450202. ISSN 0009-4609.
- ^ Zainul, Rahadian (16 August 2018). "Studi Literasi Menggunakan Endnote Dan Aplikasi Pembantu (Google Translator, Google Cendikia, Google Sites, Chemoffice 2008, east-learning, dan Snipping Tool)". doi:10.31227/osf.io/5ncpe.
- ^ "Chapter 4: Local Party Government", Local Government Institutionalization in Hungary, Peter Lang, 2015, doi:10.3726/978-3-653-05128-v/13, ISBN9783631657348
- ^ MISSING-VALUE, MISSING-VALUE (2016), "The pre-recognition menstruum (1949–1972)", Australia—China Relations mail 1949, Routledge, pp. 9–36, doi:10.4324/9781315568379-2, ISBN9781315568379
- ^ "Hong Kong Colony". www.britishempire.co.uk . Retrieved 26 November 2018.
- ^ "export.gov". www.export.gov . Retrieved 26 November 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j 1000 l m due north o p q r south t "East Asia/Southeast Asia :: Cathay — The World Factbook - Central Intelligence Agency". world wide web.cia.gov . Retrieved 25 November 2018.
- Fitzpatrick, John. 1992. "The Middle Kingdom, the Middle Bounding main, and the Geographical Pin of History". Review (fernand Braudel Center) xv (3). Research Foundation of SUNY: 477–521. https://www.jstor.org/stable/40241233.
External links [edit]
- Chinese Academy of Sciences Constitute of Geographical Sciences and Natural Resources
- Chinese Ecosystem Research Network (CERN)
- Illustrations of Famous Mountains from 1368–1644
Coordinates: 35°00′North 105°00′E / 35.000°North 105.000°Eastward / 35.000; 105.000
Map Of North China Plain,
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geography_of_China
Posted by: williamswict2001.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Map Of North China Plain"
Post a Comment